Solar Power Explained Simply
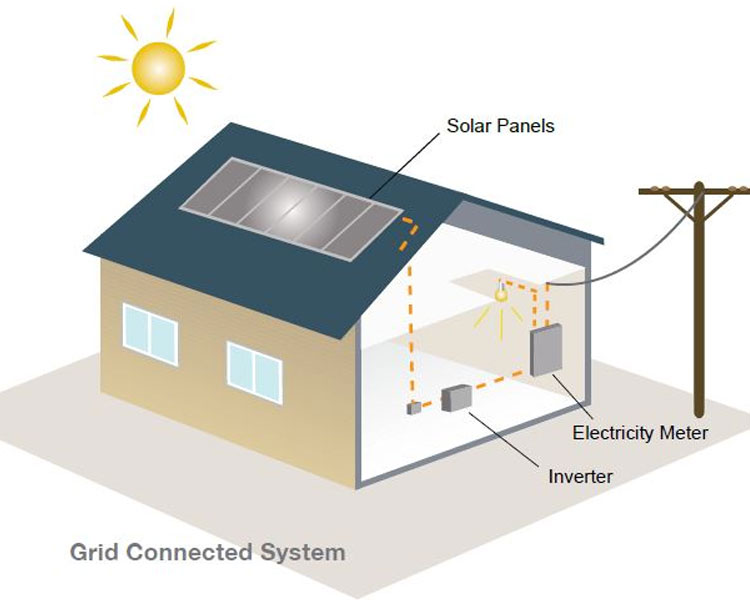
There are basically three important components of solar power system.
- Solar Panels
- Inverter
- Installation
Solar panels are installed on the roof and when exposed to sunlight they produce DC electricity. This DC electricity is sent to the inverter through the DC cabling. The inverter converts that DC electricity into usable AC electricity. This is used by the household and the appliances in it. Any electricity that is not used by the household will be transported back into the main electricity grid and a credit will be given to the homeowner on their next electricity bill for this excess power. (See feed in tariffs for more).
The installation is important because if not done correctly the panels and or roof could be damaged in high winds, bad workmanship or negligence can lead electrical fires, system performance is also affected by poorly designed and installed systems.

Because there are only three important factors involved, it is important to get these right. If the solar panels are inferior they will not produce power efficiently and the system will not produce as much electricity as it could. Inferior panels will degrade and become less efficient faster than a better quality panel. If the inverter quality is poor it will waste a lot of the energy in the conversion process resulting in less usable power and it will also not last as long. As mentioned above, if the installers cut corners on the installation it can affect the system performance as well as put home in jeopardy.
Off-Grid or Hybrid Systems
A bank of batteries can be installed in addition to the above in order to become self sufficient. This means that some of the power produced by the solar panels will be used to keep the batteries charged and the batteries will power the household in times when the solar panels can not – ie. at night or during overcast days. In most cases, the solar system will only draw from the grid when absolutely necessary.
Interested in battery storage!
